论文题目:Effects of host phylogeny, habitat and spatial proximity on host specificity and diversity of pathogenic and mycorrhizal fungi in a subtropical forest
作者:Zihui Wang, Yuan Jiang, David C. Deane, Fangliang, Wensheng Shu* & Yu Liu*
文章简介:
近三十年来,虽然普遍认为土壤病原菌和菌根真菌通过不同的寄主专化性可调控森林树种多样性,但目前我们对这两大类真菌的宿主专化性程度仍不清楚,以及对影响其群落组成的因素还缺乏实验证据。针对此现状,我们在广东黑石顶50公顷样地内采集了45个树种,共519棵树的细根,借助第二代测序平台获取了细根中病原真菌和菌根真菌的群落组成数据。利用多元线性回归,变差分解和网络分析等统计方法,分析了宿主植物谱系、性状、环境因子等因素对真菌群落影响的相对重要性并比较了两种真菌的寄主专化性程度。研究发现,寄主谱系是决定真菌群落组成最重要的因素,而且谱系的影响很大程度上是由谱系保守的植物性状引起的;病原真菌的宿主专化性明显高于菌根真菌,而且这种差异在小的寄主谱系尺度更加明显。这一结果为进一步理解植物-土壤微生物相互作用在生物多样性维持中的角色提供了基础。
作者:Zihui Wang, Yuan Jiang, David C. Deane, Fangliang, Wensheng Shu* & Yu Liu*
文章简介:
近三十年来,虽然普遍认为土壤病原菌和菌根真菌通过不同的寄主专化性可调控森林树种多样性,但目前我们对这两大类真菌的宿主专化性程度仍不清楚,以及对影响其群落组成的因素还缺乏实验证据。针对此现状,我们在广东黑石顶50公顷样地内采集了45个树种,共519棵树的细根,借助第二代测序平台获取了细根中病原真菌和菌根真菌的群落组成数据。利用多元线性回归,变差分解和网络分析等统计方法,分析了宿主植物谱系、性状、环境因子等因素对真菌群落影响的相对重要性并比较了两种真菌的寄主专化性程度。研究发现,寄主谱系是决定真菌群落组成最重要的因素,而且谱系的影响很大程度上是由谱系保守的植物性状引起的;病原真菌的宿主专化性明显高于菌根真菌,而且这种差异在小的寄主谱系尺度更加明显。这一结果为进一步理解植物-土壤微生物相互作用在生物多样性维持中的角色提供了基础。

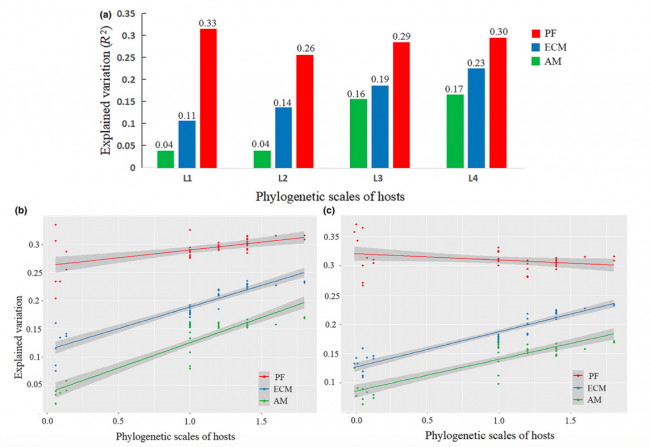
Explained variation (R2) of redundancy analysis (RDA) models of the community composition of pathogenic (PF), ectomycorrhizal (ECM) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (MF) as a function of host phylogeny at different host-phylogenetic scales, including a four-level ordinal scale (L1–L4) based on Listea (a) and numerical scales focused on Listea (b) and Lithocarpus (c).
该论文于2019年3月发表在SCI 一 区刊物New Phytologist(影响因子:7.43)上。
我学院刘宇研究员和华南师范大学束文圣教授 共同为通讯作者,王梓辉为第一作者。


